Description
Interferons (IFNs) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria, parasites, or tumor cells. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten their anti-viral defenses. Based on the type of receptor through which they signal, human interferons have been classified into three major types: interferon type I, including IFN-α, IFN-β, IFN-ε, IFN-κ and IFN-ω, interferon type II (IFN-γ in humans) and interferon type III: Signal through a receptor complex consisting of IL10R2 and IFNLR1. The IFN-α proteins are produced by leukocytes. They are mainly involved in innate immune response against viral infection. Studies suggest that by forcing IFN-α expression in tumor-infiltrating macrophages, it is possible to elicit a more effective dendritic cell activation and immune effector cell cytotoxicity. IFN-α acts as a pyrogenic factor by altering the activity of thermosensitive neurons in the hypothalamus thus causing fever. A similar mechanism is used by IFN-α to reduce pain; IFN-α interacts with the μ-opioid receptor to act as an analgesic.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.















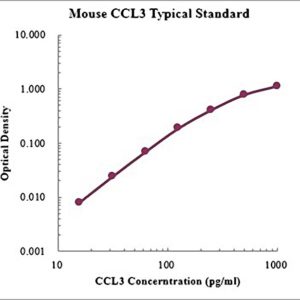

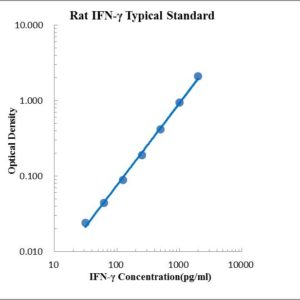
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.