Description
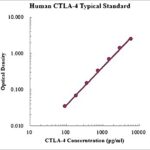
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4), also known as CD152, is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that is expressed on the surface of helper T cells. CTLA-4 is similar to the T-cell co-stimulatory protein, CD28, and both molecules bind to CD80 and CD86. CTLA-4 transmits an inhibitory signal to T cells, whereas CD28 transmits a stimulatory signal. CTLA-4 functions as an immune checkpoint, downregulates the immune system, acts as an “off” switch when bound to CD80 or CD86 on the surface of antigen-presenting cells. Intracellular CTLA-4 is also found in regulatory T cells and may be important to their function.
Mutations in this gene have been associated with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, Graves’ disease, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, celiac disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, thyroid-associated orbitopathy, primary biliary cirrhosis and other autoimmune diseases. Polymorphisms of the CTLA-4 gene are associated with autoimmune diseases such as autoimmune thyroid disease and multiple sclerosis, though this association is often weak. In systemic lupus erythematosus, the splice variant sCTLA-4 is found to be aberrantly produced and found in the serum of patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.













Reviews
There are no reviews yet.